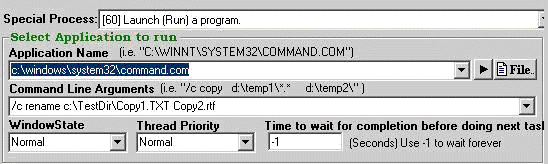
ConvertITP has the ability to launch applications allowing for a huge extension in functionality. Most commonly used programs are batch files and Command.COM, though you may choose whatever program you think will help you get your job done. Specifying command line arguments and other options are available, as discussed below.
Once you've selected special process Launch (Run) a program the screen displays the following:

Application
Name: Either type in or browse for the path and name of the application
to run. This can be any application installed on your computer or the
command interpreter. If you click the launch now button (  found at the right side of the Application
Name text box), the application specified will execute.
found at the right side of the Application
Name text box), the application specified will execute.
NOTES on using cmd.exe or command.com:
Choosing the command interpreter (command.com or cmd.exe) lets you utilize command line arguments (DOS commands). There are differences between command.com and cmd.exe on Windows NT systems having to do with environment variables. For example, using command.com limits the user to the eight-dot-three DOS naming convention whereas cmd.exe is not subject to that constraint. Thus a filename like 'totalOf8.txt' works for command.com or cmd.exe, but a lengthy name like 'totalOfTen.txt' would work only with cmd.exe. Depending on how your system is configured, you may find that command.com works in some but not all situations. If that is the case, try the same command line arguments substituting cmd.exe for the application name.
Command Line Arguments: Here you may enter arguments for the application to use when executing. For example if you specified to run Notepad.exe, you can optionally specify a text file for it to open when executing. All programs have different command line capabilities.
NOTES on specifying cmd.exe or command.com command line arguments:
Traditional DOS commands can be utilized here to do such tasks as copying, deleting, making directories, running batch files, etc. Begin each command with '/c' if a string follows. Note: Per normal DOS naming conventions, file names must not exceed eight characters plus a three character extension (e.g. 'eightchar.txt') if you are using the command.com interpreter. If the path to and name of a file is placed here without any other arguments, the application will launch and open the file.
Window State: Choose from Hidden, Normal, Maximized or Minimized. Note that some programs will override this selection and open in their initially preferred state.
Thread Priority: Choose from Idle, Normal, High Priority or Real-time Priority.
Idle |
Process whose threads run only when the system is idle. The threads of the process are preempted by the threads of any process running in a higher priority class. |
Normal |
Process with no special scheduling needs. |
High Priority |
Process that performs time-critical tasks that must be executed immediately. The threads of the process preempt the threads of normal or idle priority class processes. |
Realtime Priority |
Process that has the highest possible priority. The threads of the process preempt the threads of all other processes, including operating system processes performing important tasks. |
Time to wait for completion before doing next task: The maximum length of time in seconds a process will run before moving on to the next task in the Conversion Task list. Use -1 if you don't want to impose a time limit and wait forever for the application to exit before moving on to the next item in the Conversion Task list.
See Also:
Launch A Program: Example of cmd .exe